날짜와 시간
날짜와 시간
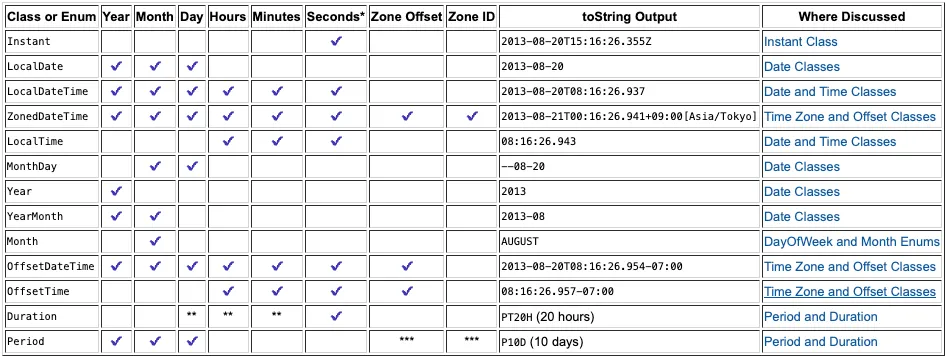
자바 날짜와 시간 라이브러리 소개
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/datetime/iso/overview.html
*: 초는 나노초 단위의 정밀도로 캡처된다. (밀리초, 나노초 가능)**: 이 클래스는 이 정보를 저장하지는 않지만 이러한 단위로 시간을 제공하는 메서드가 있다.***:ZonedDateTime에Period를 추가하면 서머타임 또는 기타 현지 시간 차이를 준수한다.
기본 날짜와 시간 - LocalDateTime
LocalDate: 날짜만 표현LocalTime: 시간만 표현LocalDateTime: LocalDate + LocalTime
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class LocalDateTimeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime nowDt = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime ofDt = LocalDateTime.of(2016, 8, 16, 8, 10, 1);
System.out.println("현재 날짜시간 = " + nowDt);
System.out.println("지정 날짜시간 = " + ofDt);
//날짜와 시간 분리
LocalDate localDate = ofDt.toLocalDate();
LocalTime localTime = ofDt.toLocalTime();
System.out.println("localDate = " + localDate);
System.out.println("localTime = " + localTime);
//날짜와 시간 합체
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(localDate, localTime);
System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);
//계산(불변)
LocalDateTime ofDtPlus = ofDt.plusDays(1000);
System.out.println("지정 날짜시간+1000d = " + ofDtPlus);
LocalDateTime ofDtPlus1Year = ofDt.plusYears(1);
System.out.println("지정 날짜시간+1년 = " + ofDtPlus1Year);
//비교
System.out.println("현재 날짜시간이 지정 날짜시간보다 이전인가? " + nowDt.isBefore(ofDt));
System.out.println("현재 날짜시간이 지정 날짜시간보다 이후인가? " + nowDt.isAfter(ofDt));
System.out.println("현재 날짜시간과 지정 날짜시간이 같은가? " + nowDt.isEqual(ofDt));
}
}
isEqual() vs equals()
isEqual(): 단순히 비교 대상이 시간적으로 같으면true를 반환- 서울의 9시와 UTC의 0시는 시간적으로 같다. 이 둘을 비교하면
true를 반환
- 서울의 9시와 UTC의 0시는 시간적으로 같다. 이 둘을 비교하면
equals(): 객체의 타입, 타임존 등등 내부 데이터의 모든 구성요소가 같아야true를 반환- 서울의 9시와 UTC의 0시는 시간적으로 같다. 이 둘을 비교하면 타임존의 데이터가 다르기 때문에
false를 반환
- 서울의 9시와 UTC의 0시는 시간적으로 같다. 이 둘을 비교하면 타임존의 데이터가 다르기 때문에
타임존 - ZonedDateTime
ZoneId
자바는 타임존을 ZoneId 클래스로 제공
타임존 목록 예시
- Europe/London
- GMT
- UTC
- US/Arizona -07:00
- America/New_York -05:00
- Asia/Seoul +09:00
- Asia/Dubai +04:00
- Asia/Istanbul +03:00
- Asia/Shanghai +08:00
- Europe/Paris +01:00
- Europe/Berlin +01:00
ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime: LocalDateTime + ZoneOffset + ZoneId
1
2
3
4
5
6
public final class ZonedDateTime {
private final LocalDateTime dateTime;
private final ZoneOffset offset;
private final ZoneId zone;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class ZonedDateTimeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZonedDateTime nowZdt = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println("nowZdt = " + nowZdt);
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.of(2030, 1, 1, 13, 30, 50);
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = ZonedDateTime.of(ldt, ZoneId.of("Asia/Seoul"));
System.out.println("zdt1 = " + zdt1);
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = ZonedDateTime.of(2030, 1, 1, 13, 30, 50, 0, ZoneId.of("Asia/Seoul"));
System.out.println("zdt2 = " + zdt2);
ZonedDateTime utcZdt = zdt2.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
System.out.println("utcZdt = " + utcZdt);
}
}
OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime: LocalDateTime + ZoneOffset- 시간대를 고려한 날짜와 시간을 표현할 때 사용한다. 여기에는 타임존은 없고, UTC로 부터의 시간 대 차이인 고정된 오프셋만 포함
1
2
3
4
public class OffsetDateTime {
private final LocalDateTime dateTime;
private final ZoneOffset offset;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class OffsetDateTimeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OffsetDateTime nowOdt = OffsetDateTime.now();
System.out.println("nowOdt = " + nowOdt);
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.of(2030, 1, 1, 13, 30, 50);
System.out.println("ldt = " + ldt);
OffsetDateTime odt = OffsetDateTime.of(ldt, ZoneOffset.of("+01:00"));
System.out.println("odt = " + odt);
}
}
기계 중심의 시간 - Instant
- UTC 기준 1970년 1월 1일 0시 0분 0초라면
seconds에 0이 들어간다 - 날짜와 시간을 계산에 사용할 때는 적합하지 않음
장점
- 시간대 독립성:
Instant는 UTC를 기준으로 하므로, 시간대에 영향을 받지 않음 - 고정된 기준점: 모든
Instant는 1970년 1월 1일 UTC를 기준
단점
- 사용자 친화적이지 않음: 날짜와 시간을 계산하고 사용하는데 필요한 기능이 부족
- 시간대 정보 부재:
Instant에는 시간대 정보가 포함되어 있지 않아, 특정 지역의 날짜와 시간으로 변환하 려면 추가적인 작업이 필요
사용 예
- 전 세계적인 시간 기준 필요 시: 로그 기록이나, 트랜잭션 타임스탬프, 서버 간의 시간 동기화 등
- 시간대 변환 없이 시간 계산 필요 시: 시간대의 변화 없이 순수하게 시간의 흐름(예: 지속 시간 계산)만을 다루고 싶을 때
- 데이터 저장 및 교환: 데이터베이스에 날짜와 시간 정보를 저장하거나, 다른 시스템과 날짜와 시간 정보를 교환할 때
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class InstantMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//생성
Instant now = Instant.now();//UTC 기준
System.out.println("now = " + now);
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.now(); // LocalDateTime은 시간대가 없어서 사용 불가
Instant from = Instant.from(zdt);
System.out.println("from = " + from);
Instant epochStart = Instant.ofEpochSecond(0); // 1970.1.1
System.out.println("epochStart = " + epochStart);
//계산
Instant later = epochStart.plusSeconds(3600);
System.out.println("later = " + later);
//조회
long laterEpochSecond = later.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println("laterEpochSecond = " + laterEpochSecond);
}
}
기간, 시간의 간격 - Period, Duration
Period: 두 날짜 사이의 간격을 년, 월, 일 단위로 나타냄Duration: 두 시간 사이의 간격을 시, 분, 초로 나타냄
Period
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class PeriodMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//생성
Period period = Period.ofDays(10);
System.out.println("period = " + period);
//계산에 사용
LocalDate currentDate = LocalDate.of(2030, 1, 1);
LocalDate plusDate = currentDate.plus(period);
System.out.println("currentDate = " + currentDate);
System.out.println("plusDate = " + plusDate);
//기간 차이
LocalDate startDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 1);
LocalDate endDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 4, 2);
Period between = Period.between(startDate, endDate);
System.out.println("기간: " + between.getMonths() + "개월 " + between.getDays() + "일");
}
}
Duration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class DurationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Duration duration = Duration.ofMinutes(30);
System.out.println("duration = " + duration);
LocalTime lt = LocalTime.of(1, 0);
System.out.println("lt = " + lt);
//계산에 사용
LocalTime plusTime = lt.plus(duration);
System.out.println("더한 시간: " + plusTime);
//시간 차이
LocalTime start = LocalTime.of(9, 0);
LocalTime end = LocalTime.of(10, 0);
Duration between = Duration.between(start, end);
System.out.println("차이: " + between.getSeconds() + "초");
System.out.println("근무 시간: " + between.toHours() + "시간" + between.toMinutesPart() + "분");
}
}
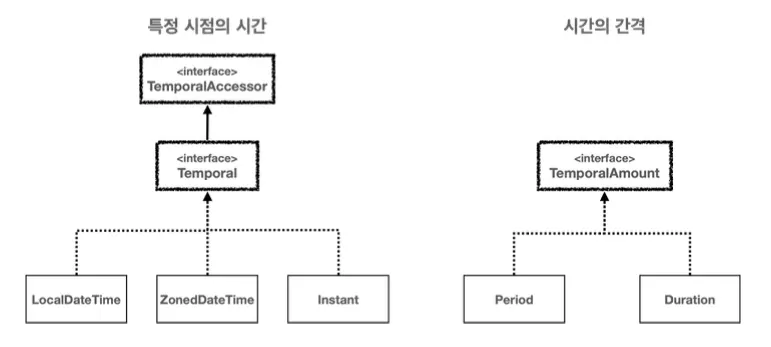
날짜와 시간의 핵심 인터페이스
- TemporalAccessor 인터페이스
- 날짜와 시간을 읽기 위한 기본 인터페이스
- 이 인터페이스는 특정 시점의 날짜와 시간 정보를 읽을 수 있는 최소한의 기능을 제공
- Temporal 인터페이스
TemporalAccessor의 하위 인터페이스로, 날짜와 시간을 조작(추가, 빼기 등)하기 위한 기능을 제공
- TemporalAmount 인터페이스
- 시간의 간격(시간의 양, 기간)을 나타내며, 날짜와 시간 객체에 적용하여 그 객체를 조정
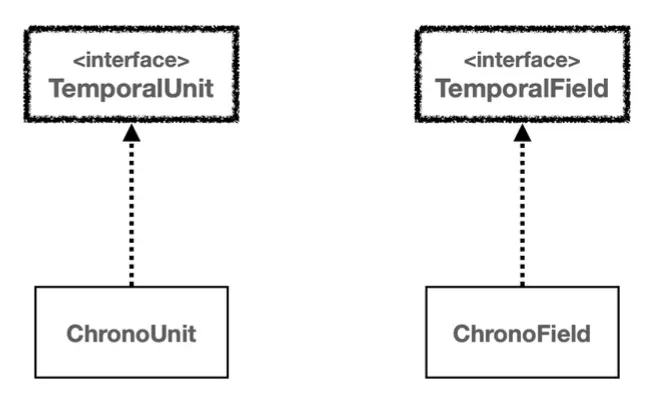
시간의 단위와 시간 필드
날짜와 시간 조회 - ChronoField
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class GetTimeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(2030, 1, 1, 13, 30, 59);
System.out.println("YEAR = " + dt.get(ChronoField.YEAR));
System.out.println("MONTH_OF_YEAR = " + dt.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR));
System.out.println("DAY_OF_MONTH = " + dt.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_DAY = " + dt.get(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_HOUR = " + dt.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR));
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_MINUTE = " + dt.get(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE));
System.out.println("편의 메서드 제공");
System.out.println("YEAR = " + dt.getYear());
System.out.println("MONTH_OF_YEAR = " + dt.getMonthValue());
System.out.println("DAY_OF_MONTH = " + dt.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("HOUR_OF_DAY = " + dt.getHour());
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_HOUR = " + dt.getMinute());
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_MINUTE = " + dt.getSecond());
System.out.println("편의 메서드에 없음");
System.out.println("MINUTE_OF_DAY = " + dt.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_DAY));
System.out.println("SECOND_OF_DAY = " + dt.get(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_DAY));
}
}
날짜와 시간 조작 - ChronoUnit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class ChangeTimePlusMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 1, 1, 13, 30, 59);
System.out.println("dt = " + dt);
LocalDateTime plusDt1 = dt.plus(10, ChronoUnit.YEARS);
System.out.println("plusDt1 = " + plusDt1);
LocalDateTime plusDt2 = dt.plusYears(10);
System.out.println("plusDt2 = " + plusDt2);
Period period = Period.ofYears(10);
LocalDateTime plusDt3 = dt.plus(period);
System.out.println("plusDt3 = " + plusDt3);
LocalDateTime changedDt1 = dt.with(ChronoField.YEAR, 2020);
System.out.println("changedDt1 = " + changedDt1);
LocalDateTime changedDt2 = dt.withYear(2020);
System.out.println("changedDt2 = " + changedDt2);
}
}
TemporalAdjuster
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class ChangeTimeWithMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 1, 1, 13, 30, 59);
//다음주 금요일
LocalDateTime with1 = dt.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.FRIDAY));
System.out.println("기준 날짜: " + dt);
System.out.println("다음 금요일: " + with1);
//이번 달의 마지막 일요일
LocalDateTime with2 = dt.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastInMonth(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY));
System.out.println("같은 달의 마지막 일요일 = " + with2);
}
}
날짜와 시간 문자열 파싱과 포맷팅
- 포맷팅: Date → String
- 파싱: String → Date
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class FormattingMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 포맷팅: 날짜와 시간을 문자로
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.of(2024, 12, 31, 13, 30, 59);
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDateTime = now.format(formatter);
System.out.println("날짜와 시간 포맷팅: " + formattedDateTime);
// 파싱: 문자를 날짜와 시간으로
String dateTimeString = "2030-01-01 11:30:00";
LocalDateTime parsedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(dateTimeString, formatter);
System.out.println("문자열 파싱 날짜와 시간: " + parsedDateTime);
}
}
💡
DateTimeFormatter패턴 공식 사이트https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/time/format/DateTimeFormatter.html#patterns
참고
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.