클라이언트 → 서버 간 데이터 통신
단일 데이터 통신
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class ClientV1 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("클라이언트 시작");
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", PORT);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
log("소캣 연결: " + socket);
// 서버에게 문자 보내기
String toSend = "Hello";
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client -> server: " + toSend);
// 서버로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client <- server: " + received);
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public class ServerV1 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("서버 시작");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT);
log("서버 소켓 시작 - 리스닝 포트: " + PORT);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
log("소켓 연결: " + socket);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
// 클라이언트로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client -> server: " + received);
// 클라이언트에게 문자 보내기
String toSend = received + " World!";
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client <- server: " + toSend);
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
|
여러번 통신
while 문을 추가 해주면 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class ClientV2 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("클라이언트 시작");
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", PORT);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
log("소캣 연결: " + socket);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print("전송 문자: ");
String toSend = scanner.nextLine();
// 서버에게 문자 보내기
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client -> server: " + toSend);
if (toSend.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 서버로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client <- server: " + received);
}
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public class ServerV2 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("서버 시작");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT);
log("서버 소켓 시작 - 리스닝 포트: " + PORT);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
log("소켓 연결: " + socket);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true) {
// 클라이언트로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client -> server: " + received);
if (received.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 클라이언트에게 문자 보내기
String toSend = received + " World!";
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client <- server: " + toSend);
}
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
|
여러 클라이언트 대응
위 코드는 먼저 연결한 첫 클라이언트에게만 서버가 응답을 보내주고 있습니다.
이제 여러 클라이언트 연결 처리를 해보도록 하겠습니다.
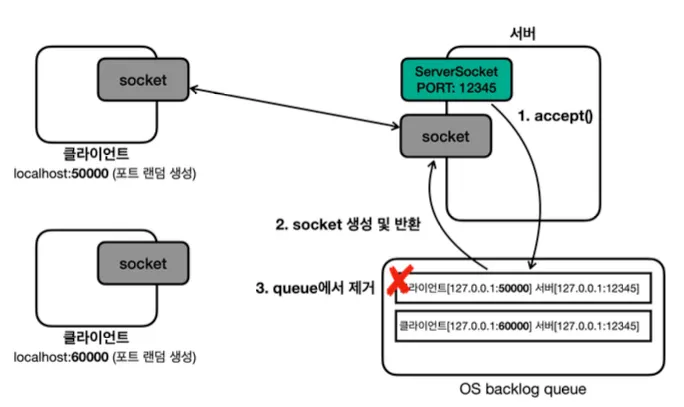
소켓 연결 원리
ServerSocket.accept()를 호출- OS backlog queueOS에서 socket을 생성 및 반환
- OS backlog queue에서 제거
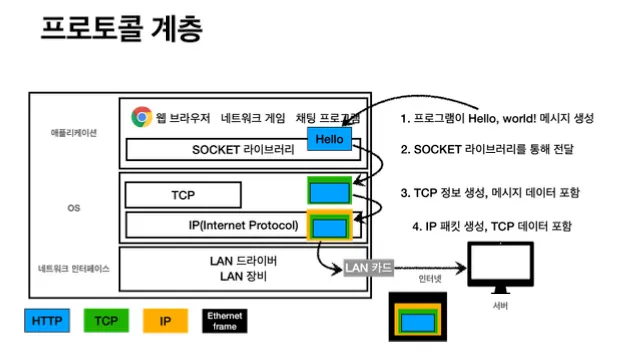
데이터 통신 원리
- 클라이언트
- 애플리케이션 → OS TCP 송신 버퍼 - > 클라이언트 네트워크 카드
- 클라이언트가 보낸 메시지가 서버에 도착했을 때, 서버
- 서버 네트워크 카드 → OS TCP 수신 버퍼 → 애플리케이션
소켓 객체 없이 서버 소켓만으로도 TCP 연결은 완료 됩니다.
단, 데이터를 통신 하려면 소켓 객체가 필요합니다.
코드
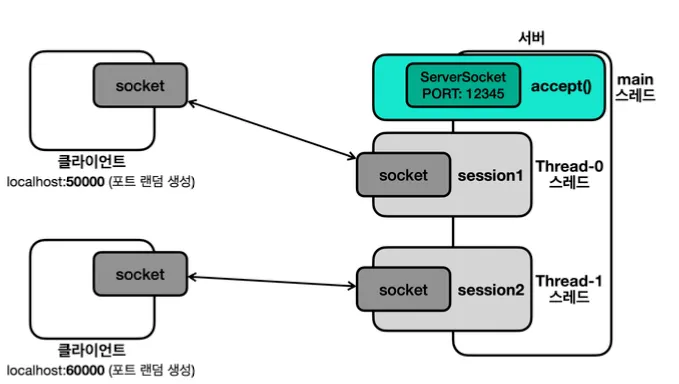
서버는 계속 해서 소켓을 받고 받은 소켓을 스레드 별로 처리하도록 해야 여러 클라이언트를 처리할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class ClientV3 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("클라이언트 시작");
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", PORT);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
log("소캣 연결: " + socket);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print("전송 문자: ");
String toSend = scanner.nextLine();
// 서버에게 문자 보내기
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client -> server: " + toSend);
if (toSend.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 서버로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client <- server: " + received);
}
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public class SessionV3 implements Runnable {
private final Socket socket;
public SessionV3(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true) {
// 클라이언트로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client -> server: " + received);
if (received.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 클라이언트에게 문자 보내기
String toSend = received + " World!";
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client <- server: " + toSend);
}
// 자원 정리
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
input.close();
output.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class ServerV3 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("서버 시작");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT);
log("서버 소켓 시작 - 리스닝 포트: " + PORT);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 블로킹
log("소켓 연결: " + socket);
SessionV3 session = new SessionV3(socket);
Thread thread = new Thread(session);
thread.start();
}
}
}
|
자원 정리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class ResourceV1 {
private String name;
public ResourceV1(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void call() {
System.out.println(name + " call");
}
public void callEx() throws CallException {
System.out.println(name + " callEx");
throw new CallException(name + " ex");
}
public void close() {
System.out.println(name + " close");
}
public void closeEx() throws CloseException {
System.out.println(name + " closeEx");
throw new CloseException(name + " ex");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class ResourceV2 implements AutoCloseable {
private String name;
public ResourceV2(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void call() {
System.out.println(name + " call");
}
public void callEx() throws CallException {
System.out.println(name + " callEx");
throw new CallException(name + " ex");
}
@Override
public void close() throws CloseException {
System.out.println(name + " close");
throw new CloseException(name + " ex");
}
}
|
일반적인 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public class ResourceCloseMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
logic();
} catch (CallException e) {
System.out.println("CallException 예외 처리");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (CloseException e) {
System.out.println("CloseException 예외 처리");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static void logic() throws CallException, CloseException {
ResourceV1 resource1 = null;
ResourceV1 resource2 = null;
try {
resource1 = new ResourceV1("resource1"); // EX
resource2 = new ResourceV1("resource2");
resource1.call();
resource2.callEx(); // CallException
} catch (CallException e) {
System.out.println("ex: " + e);
throw e;
} finally {
if (resource2 != null) {
try {
resource2.closeEx(); // CloseException 발생
} catch (CloseException e) {
// close()에서 발생한 예외는 버린다. 필요하면 로깅 정도
System.out.println("close ex: " + e);
}
}
if (resource1 != null) {
try {
resource1.closeEx();
} catch (CloseException e) {
System.out.println("close ex: " + e);
}
}
}
}
}
|
아쉬운 부분
resource 변수를 선언하면서 동시에 할당 할 수 없음catch 이후에 finally 호출로 자원 정리가 조금 늦어짐- 개발자가 실수로
close()를 호출하지 않을 가능성 - 개발자가
close() 호출 순서를 실수 할 수 있음 (보통 자원을 생성한 순서와 반대로 닫아야 함)
try-with-resources
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class ResourceCloseMainV4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
logic();
} catch (CallException e) {
System.out.println("CallException 예외 처리");
Throwable[] suppressed = e.getSuppressed();
for (Throwable throwable : suppressed) {
System.out.println("suppressedEx = " + throwable);
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (CloseException e) {
System.out.println("CloseException 예외 처리");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static void logic() throws CallException, CloseException {
try (ResourceV2 resource1 = new ResourceV2("resource1");
ResourceV2 resource2 = new ResourceV2("resource2")) {
resource1.call();
resource2.callEx(); // CallException
} catch (CallException e) {
System.out.println("ex: " + e);
throw e;
}
}
}
|
장점
- 리소스 누수 방지: 모든 리소스가 제대로 닫히도록 보장
- 코드 간결성 및 가독성 향상: 명시적인
close() 호출이 필요 없어 코드가 더 간결하고 읽기 쉬워짐 - 스코프 범위 한정
- 조금 더 빠른 자원 해제:
try블럭이 끝나면 close()가 실행되고 catch가 실행 됨 - 자원 정리 순서: 먼저 선언한 자원을 나중에 정리
- 부가 예외 포함
try-with-resources는 핵심 예외를 반환- 부가 예외는 핵심 예외 안에
Suppressed로 담아서 반환
서버 정상 종료 시 자원 정리
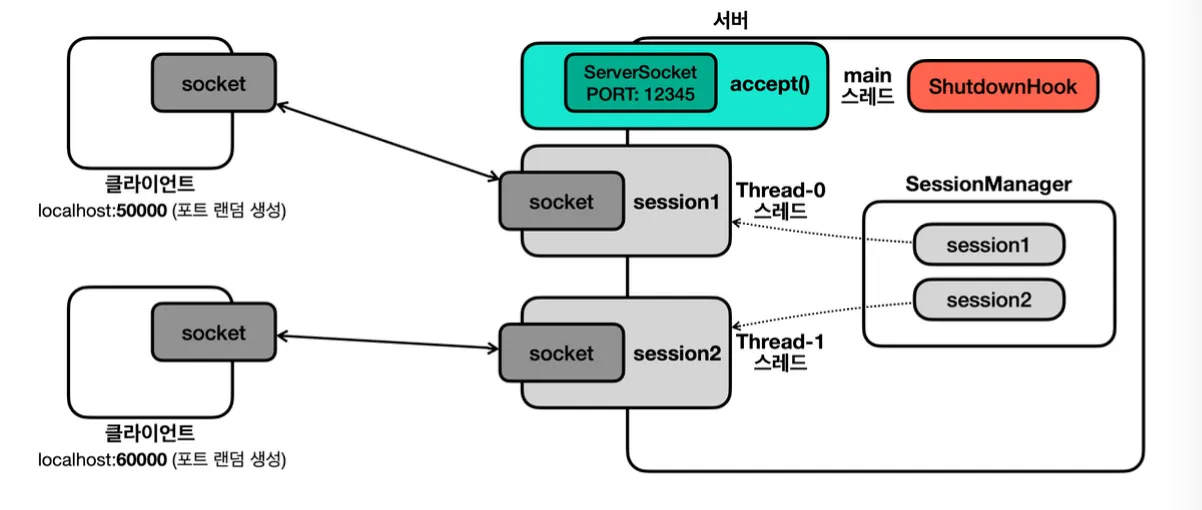
서버에 연결된 클라이언트들 모두 자원 정리를 해야 하므로, 세션을 관리할 세션 매니저가 필요합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class SocketCloseUtil {
public static void closeAll(Socket socket, InputStream input, OutputStream output) {
close(input);
close(output);
close(socket);
}
public static void close(InputStream input) {
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public static void close(OutputStream output) {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public static void close(Socket socket) {
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class ClientV6 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("클라이언트 시작");
try (Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", PORT);
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream())) {
log("소캣 연결: " + socket);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print("전송 문자: ");
String toSend = scanner.nextLine();
// 서버에게 문자 보내기
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client -> server: " + toSend);
if (toSend.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 서버로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client <- server: " + received);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log(e);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class SessionManagerV6 {
private List<SessionV6> sessions = new ArrayList<>();
public synchronized void add(SessionV6 session) {
sessions.add(session);
}
public synchronized void remove(SessionV6 session) {
sessions.remove(session);
}
public synchronized void closeAll() {
for (SessionV6 session : sessions) {
session.close();
}
sessions.clear();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| public class SessionV6 implements Runnable {
private final Socket socket;
private final DataInputStream input;
private final DataOutputStream output;
private final SessionManagerV6 sessionManager;
private boolean closed = false;
public SessionV6(Socket socket, SessionManagerV6 sessionManager) throws IOException {
this.socket = socket;
this.input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
this.output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
this.sessionManager = sessionManager;
this.sessionManager.add(this);
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 클라이언트로부터 문자 받기
String received = input.readUTF();
log("client -> server: " + received);
if (received.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
// 클라이언트에게 문자 보내기
String toSend = received + " World!";
output.writeUTF(toSend);
log("client <- server: " + toSend);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log(e);
} finally {
sessionManager.remove(this);
close();
}
}
// 세션 종료시, 서버 종료시 동시에 호출될 수 있다.
public synchronized void close() {
if (closed) {
return;
}
closeAll(socket, input, output); // shutdown
closed = true;
log("연결 종료: " + socket);
}
}
|
try-with-resources는 try가 끝나는 시점에 정리합니다. 하지만 지금은 서버를 종료하는 시점에도 Session이 사용하는 자원을 정리해야 하므로 try-with-resources를 통해 처리 할 수 없습니다.
셧다운 훅(Shutdown Hook)
자바는 프로세스가 종료될 때 자원 정리나 로그 기록과 같은 종료 작업을 마무리 할 수 있는 셧다운 훅이라는 기능을 지원합니다.
정상 종료
- 모든 non 데몬 스레드의 실행 완료로 자바 프로세스 정상 종료
- 사용자가 Ctrl+를 눌러서 프로그램 중단
kill 명령 전달(kill -9 제외)- intellij의 stop 버튼
강제 종료
- 운영체제에서 프로세스를 더 이상 유지할 수 없다고 판단할 때 사용
- 리눅스/유닉스의
kill -9나 windows의 taskkill /F
코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| public class ServerV6 {
private static final int PORT = 12345;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
log("서버 시작");
SessionManagerV6 sessionManager = new SessionManagerV6();
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT);
log("서버 소켓 시작 - 리스닝 포트: " + PORT);
// ShutdownHook 등록
ShutdownHook shutdownHook = new ShutdownHook(serverSocket, sessionManager);
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(shutdownHook, "shutdown"));
try {
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 블로킹
log("소켓 연결: " + socket);
SessionV6 session = new SessionV6(socket, sessionManager);
Thread thread = new Thread(session);
thread.start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log("서버 소켓 종료: " + e);
}
}
static class ShutdownHook implements Runnable {
private final ServerSocket serverSocket;
private final SessionManagerV6 sessionManager;
public ShutdownHook(ServerSocket serverSocket, SessionManagerV6 sessionManager) {
this.serverSocket = serverSocket;
this.sessionManager = sessionManager;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log("shutdownHook 실행");
try {
sessionManager.closeAll(); // 서버의 모든 소켓 자원 정리
serverSocket.close(); // 서버 소켓 자원 정리
Thread.sleep(1000); // 자원 정리 대기
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("e = " + e);
}
}
}
}
|
네트워크 예외
연결 예외
UnknownHostExceptionConnectException: Connection refused
타임 아웃 예외
1
2
3
4
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket();
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("192.168.1.250", 45678), 1000);
}
|
ConnectException: Operation timed out- IP는 존재하나 해당 IP를 사용하는 서버가 없을 때 발생하는 에러
- 서버가 너무 바쁘거나 문제가 있을 때 발생하는 에러
소켓 타임아웃
read 타임아웃
1
2
3
| socket.setSoTimeout(3000); // 타임아웃 시간 설정
int read = input.read(); // 기본은 무한 대기
|
SocketTimeoutException: Read timed out- 설정한 시간 내에 응답이 오지 않으면 발생하는 에러
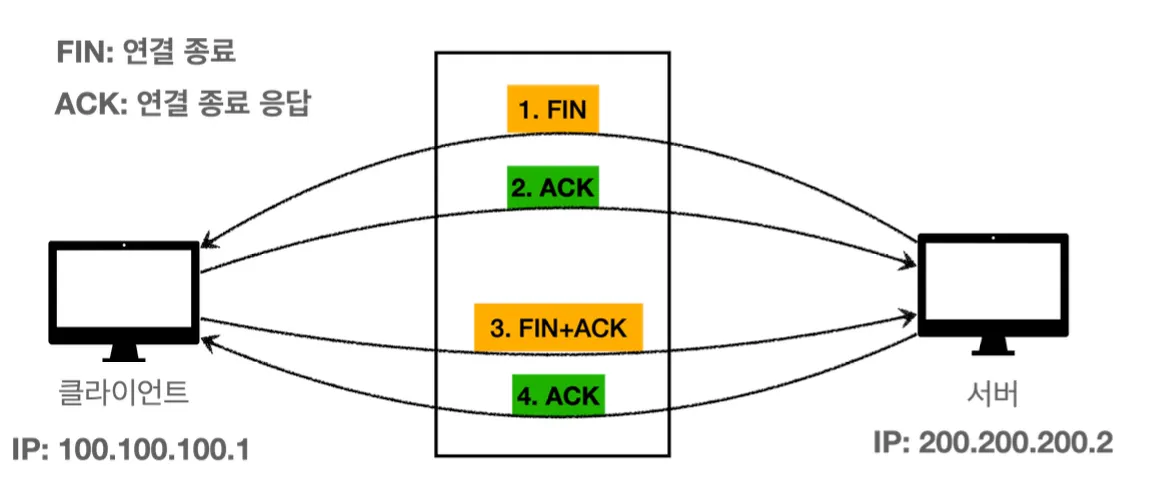
정상 종료
socket.close()를 호출하면 TCP에서 종료의 의미인 FIN 패킷을 상대방에게 전달
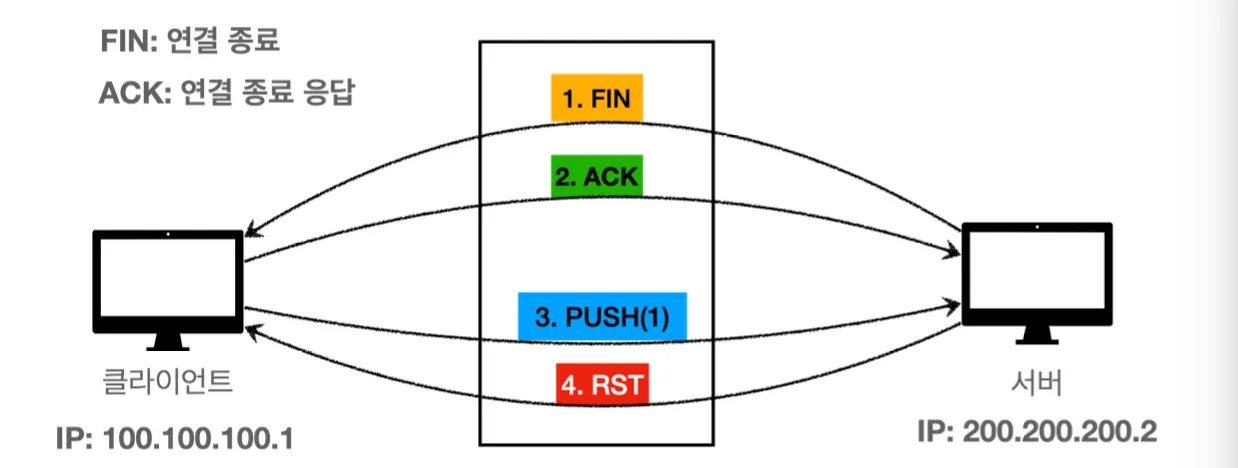
강제 종료
- TCP 연결 중에 문제가 발생하면 RST 라는 패킷이 발생
RST패킷이 도착한 뒤 read()로 메시지를 읽을 때
SocketException: Connection reset
RST 패킷이 도착한 뒤 write()로 메시지를 전송할 때
SocketException: Broken pipe
RST(Rest)란?
- TCP에서 RST 패킷은 연결 상태를 초기화 해서 더 이상 현재의 연결을 유지하지 않겠다는 의미를 전달
- 여기서 Reset은 현재의 세션을 강제로 종료하고, 연결을 무효화 하라는 뜻
- RST 패킷은 TCP 연결에 문제가 있는 다양한 상황에 발생
- TCP 스펙에 맞지 않는 순서로 메시지가 전달될 때
- TCP 버퍼에 있는 데이터를 아직 다 읽지 않았는데, 연결을 종료 할 때
- 방화벽 같은 곳에서 연결을 강제로 종료할 때 등
IOException으로 대부분 처리하고, 필요에 따라 세부적인 예외 처리를 하면 됩니다.
참고