List
List
List
- 순서 보장 O
- 중복 허용 O
- 각 요소는 인덱스를 통해 접근 가능. 0부터 시작
순서가 중요하거나 중복된 요소를 허용해야 하는 경우에 주로 사용
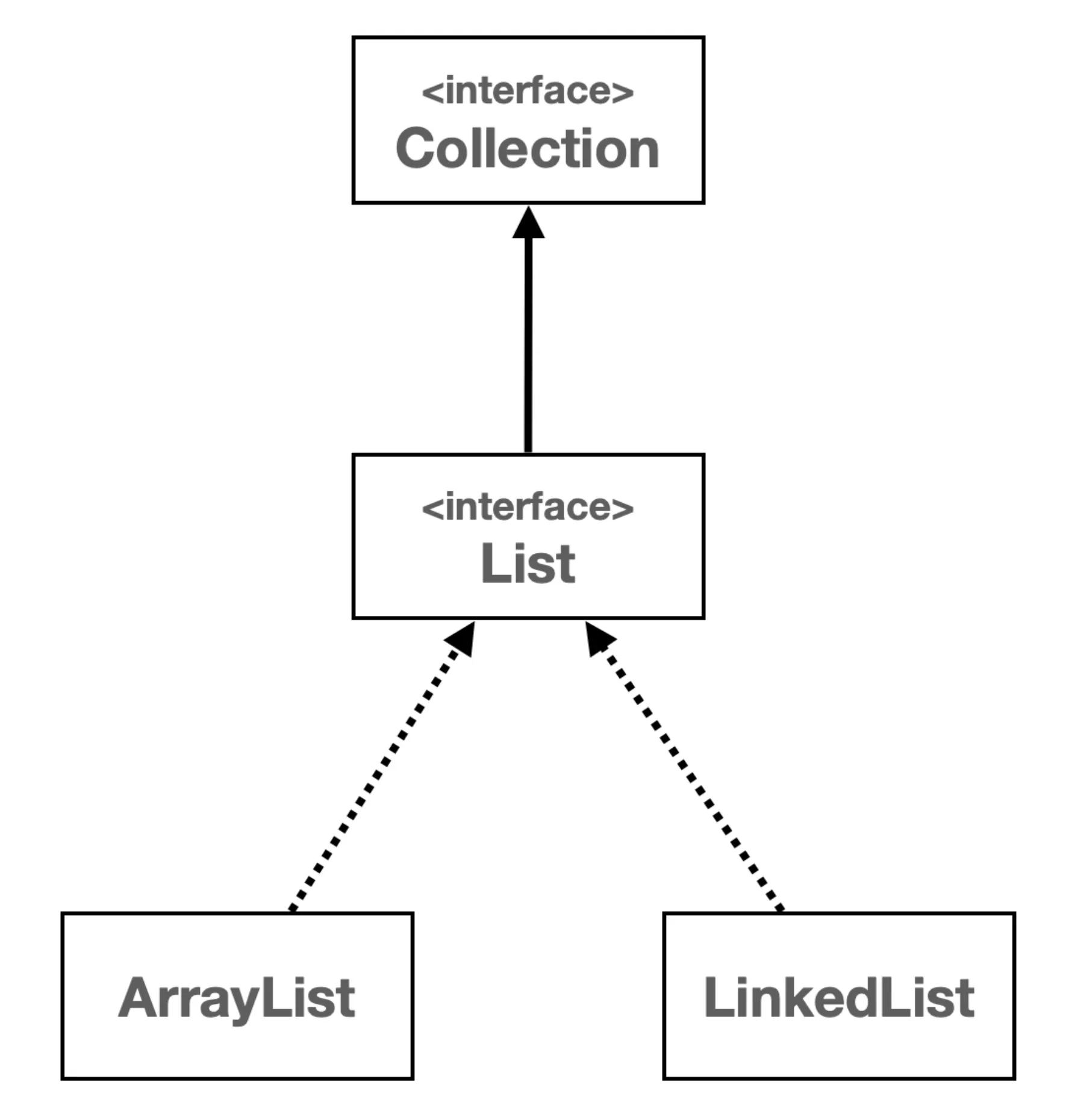
상속 구조
Collection 인터페이스
- 데이터 그룹을 다루기 위한 메서드를 정의
List,Set,Queue와 같은 다양한 하위 인터페이스와 함께 사용
List 인터페이스
- 순서가 있는 컬렉션
- 같은 객체 중복 저장 허용
- 크기가 동적으로 변화하는 컬렉션을 다룰 때 유연하게 사용
ArrayList
특징
- 배열을 사용해서 데이터 관리
- 기본
CAPACITY= 10CAPACITY를 넘어가면 배열을 50% 증가
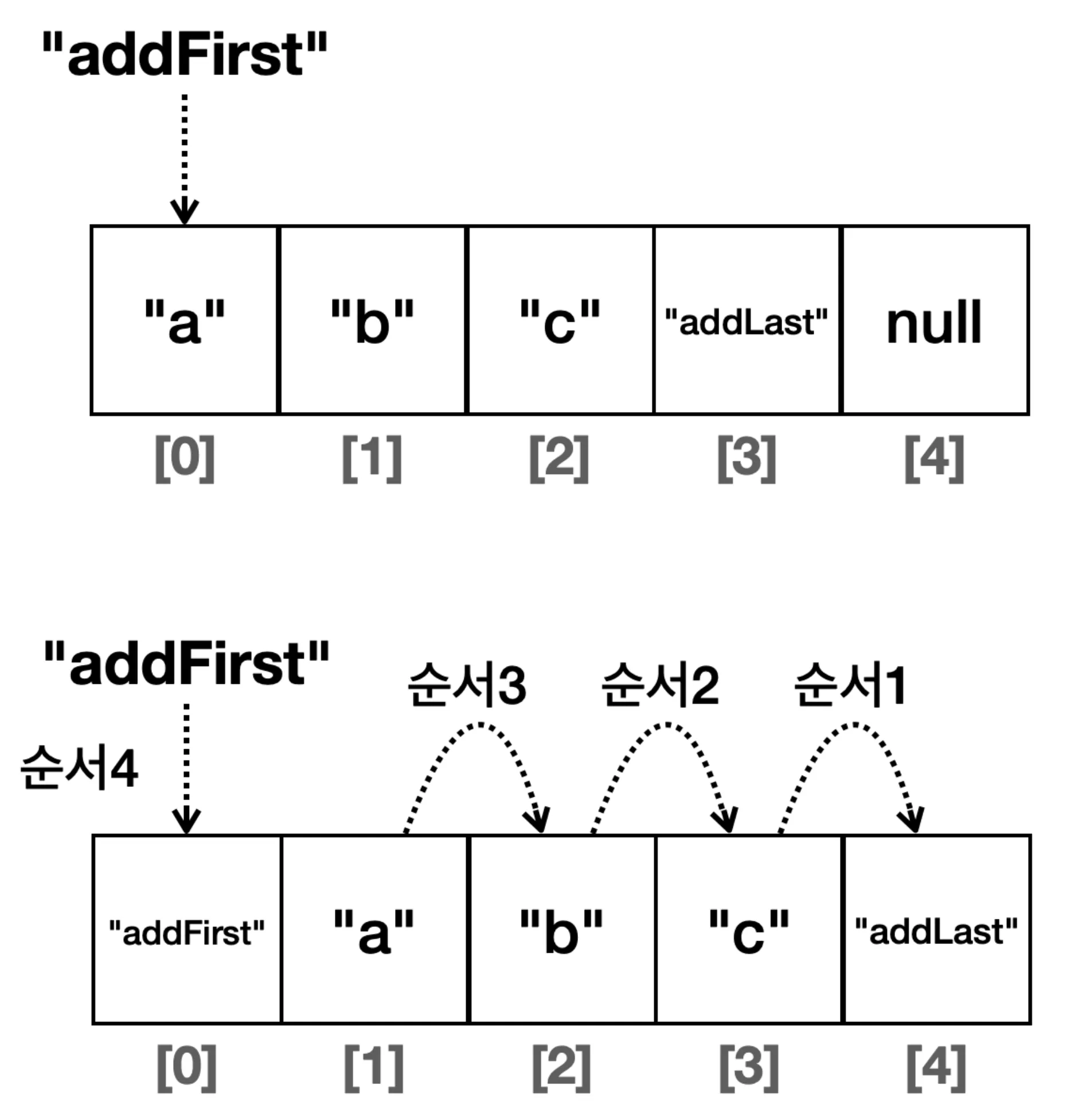
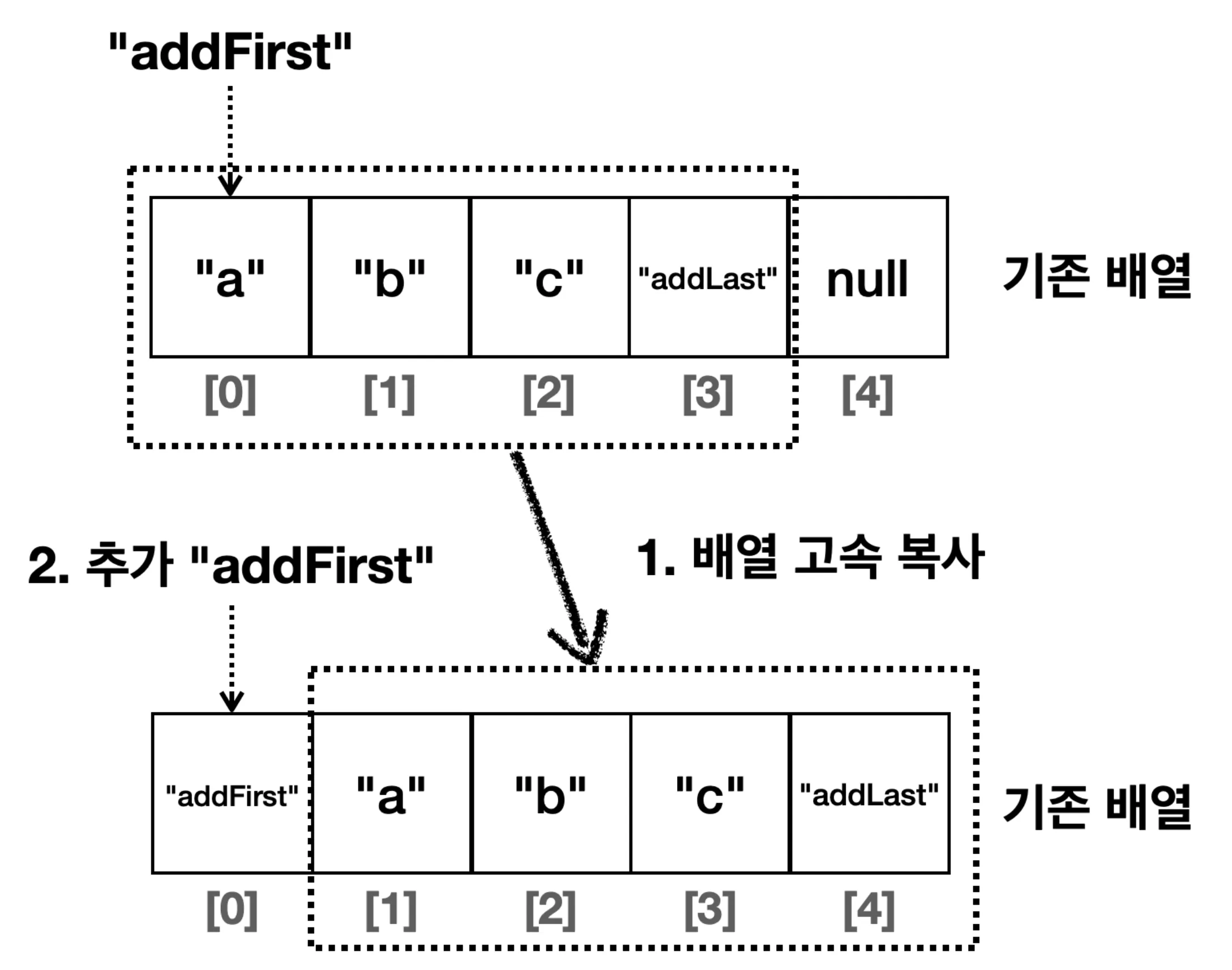
- 메모리 고속 복사 연산을 사용
System.arraycopy()를 이용하여 요소를 한 칸씩 이동 시키는 것을 최적화하여 비교적 빠르게 수행- 메모리 고속 복사 연산 사용
- 메모리 고속 복사 연산 사용
LinkedList
특징
- 이중 연결 리스트 구조
첫 번째 노드와 마지막 노드 둘 다 참조
- 단일 연결 리스트
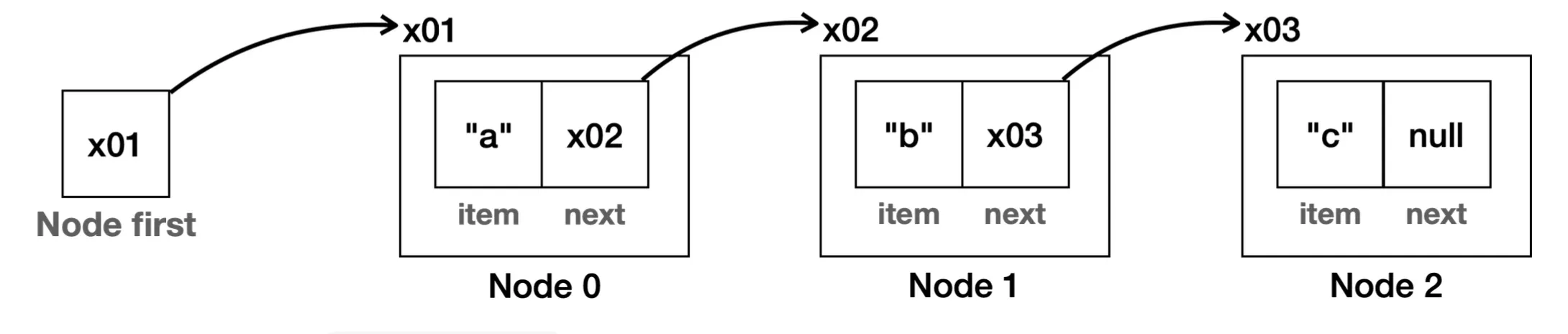
- 이전 노드로 이동할 수 없음
- 이중 연결 리스트
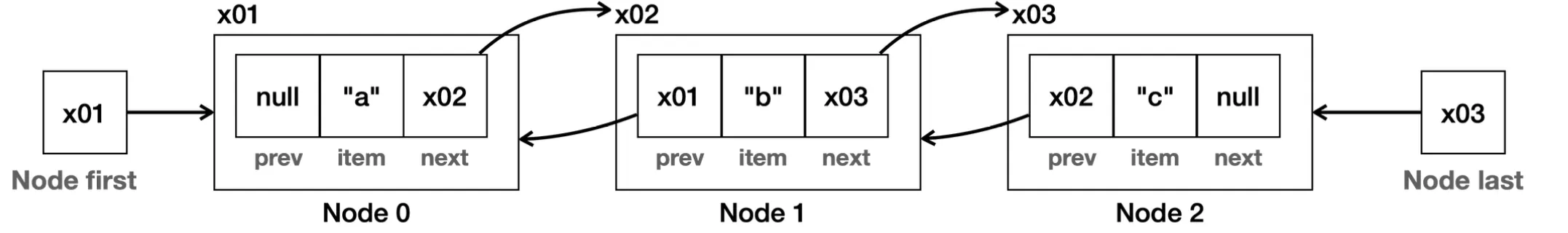
- 다음 노드, 이전 노드 둘 다 이동 가능
- 마지막 노드에 대한 참조를 제공하기 때문에 데이터를 마지막에 추가해도 O(1)의 성능을 제공
- 인덱스가 사이즈의 절반 이하면 처음부터 찾고 절반을 넘으면 마지막 노드부터 역방향으로 조회해서 조회 성능 최적화
성능 비교
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
public class JavaListPerformanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 50_000;
System.out.println("==ArrayList 추가==");
addFirst(new ArrayList<>(), size);
addMid(new ArrayList<>(), size);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); //조회용 데이터로 사용
addLast(arrayList, size);
System.out.println("==LinkedList 추가==");
addFirst(new LinkedList<>(), size);
addMid(new LinkedList<>(), size);
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); //조회용 데이터로 사용
addLast(linkedList, size);
int loop = 10000;
System.out.println("==ArrayList 조회==");
getIndex(arrayList, loop, 0);
getIndex(arrayList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(arrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==LinkedList 조회==");
getIndex(linkedList, loop, 0);
getIndex(linkedList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(linkedList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==ArrayList 검색==");
search(arrayList, loop, 0);
search(arrayList, loop, size / 2);
search(arrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==LinkedList 검색==");
search(linkedList, loop, 0);
search(linkedList, loop, size / 2);
search(linkedList, loop, size - 1);
}
private static void addFirst(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(0, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("앞에 추가 - 크기: " + size + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void addMid(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i / 2, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("평균 추가 - 크기: " + size + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void addLast(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("뒤에 추가 - 크기: " + size + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void getIndex(List<Integer> list, int loop, int index) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.get(index);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("index: " + index + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void search(List<Integer> list, int loop, int findValue) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.indexOf(findValue);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("findValue: " + findValue + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
==ArrayList 추가==
앞에 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 133ms
평균 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 63ms
뒤에 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 3ms
==LinkedList 추가==
앞에 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 4ms
평균 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 1111ms
뒤에 추가 - 크기: 50000, 계산 시간: 5ms
==ArrayList 조회==
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
==LinkedList 조회==
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 408ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
==ArrayList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 129ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 257ms
==LinkedList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 495ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 983ms
| 기능 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| 앞에 추가, 삭제 | O(n) - 133ms | O(1) - 4ms |
| 평균 추가,삭제 | O(n) - 63ms | O(n) - 1111ms |
| 뒤에 추가, 삭제 | O(1) - 3ms | O(1) - 5ms |
| 인덱스 조회 | O(1) - 0ms | O(n) - 평균 408ms |
| 검색 | O(n) - 평균 129ms | O(n) - 평균 495ms |
시간 복잡도와 실제 성능
- 이론적으로
LinkedList의 중간 삽입 연산은ArrayList보다 빠를 수 있습니다. 그러나 실제 성능은 순차 접근 속도, 메모리 할당 및 해제 비용, CPU 캐시 활용도 등 다양한 요소에 의해 영향을 받습니다.- 추가로
ArrayList는 메모리 고속 복사를 사용하여 최적화 합니다.
- 추가로
LinkedList는 각 요소가 별도의 객체로 존재하고 다음 요소의 참조를 저장하기 때문에 CPU 캐시 효율이 떨어지고, 메모리 접근 속도가 상대적으로 느려질 수 있습니다.
ArrayList vs LinkedList 실무에서의 사용
- 대부분의 경우
ArrayList가 성능상 유리하기 때문에 주로ArrayList를 사용 - 만약 데이터를 앞쪽에서 자주 추가하거나 삭제할 일이 있다면
LinkedList를 고려- 이 마저도 데이터가 많을 때
참고
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.